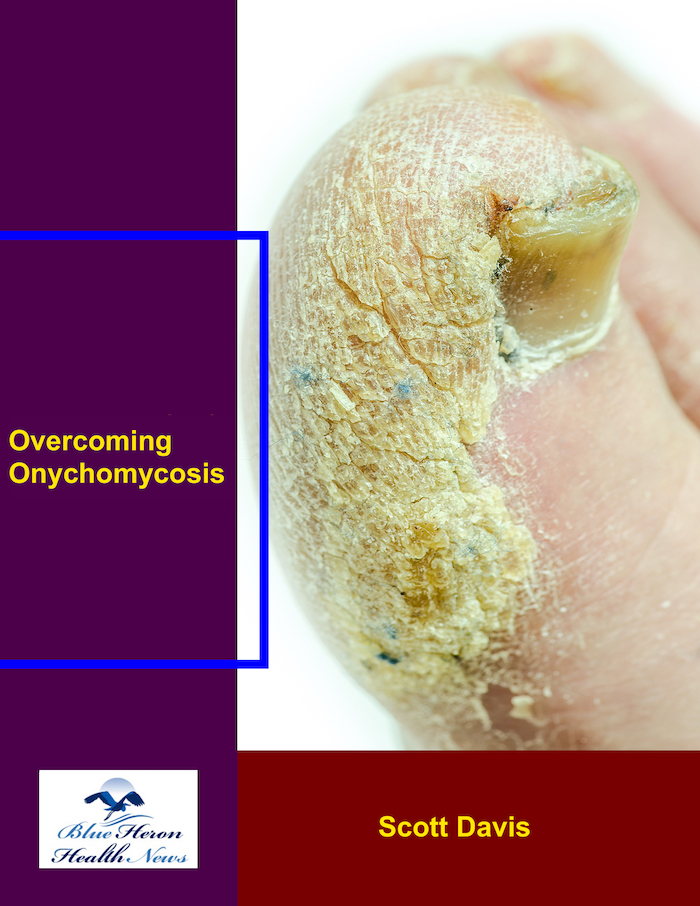
Overcoming Onychomycosis™ By Scott Davis If you want a natural and proven solution for onychomycosis, you should not look beyond Overcoming Onychomycosis. It is easy to follow and safe as well. You will not have to take drugs and chemicals. Yes, you will have to choose healthy foods to treat your nail fungus. You can notice the difference within a few days. Gradually, your nails will look and feel different. Also, you will not experience the same condition again!
How is the dosage of oral antifungal medication determined?
The dosage of oral antifungal medication for treating onychomycosis is determined based on several key factors to ensure effectiveness while minimizing side effects. Here’s how healthcare providers typically decide on the dose:
Factors Influencing Oral Antifungal Dosage for Onychomycosis
1. Type of Antifungal Drug
Different antifungals have specific recommended dosages based on clinical trials.
Common drugs like terbinafine and itraconazole have standardized dosing regimens.
2. Patient’s Age and Weight
Dosages may be adjusted for children or individuals with low body weight.
Standard adult doses apply unless special considerations exist.
3. Severity and Location of Infection
Toenail infections often require longer treatment than fingernail infections.
More severe or extensive infections may influence the duration rather than the dose per day.
4. Liver and Kidney Function
Since these medications are metabolized by the liver, impaired liver function may require dose adjustments or alternative therapies.
Kidney function can also affect drug clearance.
5. Potential Drug Interactions
Some antifungals interact with other medications, affecting dosing decisions.
6. Treatment Duration
The daily dose is typically fixed, but the total duration varies:
Terbinafine: Usually 250 mg once daily for 6 weeks (fingernails) to 12 weeks (toenails).
Itraconazole: Often given as pulse therapy (e.g., 200 mg twice daily for one week per month) or continuous dosing for several weeks.
Typical Dosage Examples
Medication Standard Adult Dose Duration
Terbinafine 250 mg once daily 6 weeks (fingernails), 12 weeks (toenails)
Itraconazole 200 mg twice daily (continuous) or pulse dosing (e.g., 200 mg twice daily for 1 week/month) 6–12 weeks depending on regimen and nail affected
Fluconazole 150–300 mg once weekly (off-label) Several months
Summary Table
Factor Impact on Dosage
Drug type Determines standard dose guidelines
Patient weight/age May require adjustments
Infection severity Affects duration more than dose
Liver/kidney function May require dose reduction or monitoring
Drug interactions Influences choice and dosing
In brief: The dosage of oral antifungal medication for onychomycosis is guided by the specific drug’s standard protocols, patient characteristics, infection severity, and organ function, with the daily dose usually fixed and treatment duration tailored to infection site and response.
Long-term oral antifungal therapy—often needed for stubborn or systemic fungal infections—can be effective but carries several potential risks and complications that require careful monitoring. Here’s an overview:
Risks of Long-Term Oral Antifungal Therapy
Liver Toxicity
Prolonged use can strain the liver, leading to elevated liver enzymes, hepatitis, or even liver failure in rare cases.
Regular liver function tests (LFTs) are essential during therapy.
Drug Interactions
Many antifungals affect cytochrome P450 enzymes, altering the metabolism of other medications (e.g., blood thinners, statins, certain heart or seizure drugs).
This can increase toxicity or reduce effectiveness of other drugs.
Resistance Development
Long-term use may encourage fungal resistance, making infections harder to treat.
Adverse Effects Accumulation
Prolonged exposure increases risk of side effects like gastrointestinal upset, skin reactions, and taste disturbances.
Blood Disorders
Rarely, long-term therapy may cause bone marrow suppression, leading to anemia, neutropenia, or thrombocytopenia.
Blood count monitoring is recommended for extended use.
Cardiac Risks (especially with itraconazole)
Potential for congestive heart failure or negative effects on heart rhythm in susceptible individuals.
Photosensitivity (notably with griseofulvin)
Increased risk of sunburn or skin damage with sun exposure.
Monitoring Recommendations for Long-Term Therapy
Parameter Monitoring Frequency
Liver function tests (LFTs) Every 1–3 months
Complete blood count (CBC) Periodically, especially if symptoms develop
Drug interactions review Before starting and during therapy
Clinical symptoms Ongoing monitoring for side effects
Summary Table
Risk Description Prevention/Monitoring
Liver toxicity Liver damage from prolonged drug exposure Regular LFTs, dose adjustment
Drug interactions Altered metabolism of other drugs Medication review, adjust doses
Resistance development Fungal adaptation reducing drug effectiveness Use appropriate duration and drugs
Accumulated side effects Increased GI, skin, and neurological symptoms Monitor symptoms, supportive care
Blood disorders Rare bone marrow suppression CBC monitoring if prolonged therapy
Cardiac risks Heart failure risk (esp. itraconazole) Cardiac evaluation if indicated
Photosensitivity Sunburn risk (griseofulvin) Sun protection, limit sun exposure
Would you like advice on how to safely manage long-term antifungal treatment or alternatives if risks outweigh benefits?
Overcoming Onychomycosis™ By Scott Davis If you want a natural and proven solution for onychomycosis, you should not look beyond Overcoming Onychomycosis. It is easy to follow and safe as well. You will not have to take drugs and chemicals. Yes, you will have to choose healthy foods to treat your nail fungus. You can notice the difference within a few days. Gradually, your nails will look and feel different. Also, you will not experience